Signs indicating diabetic neuropathy caused by excess sugar
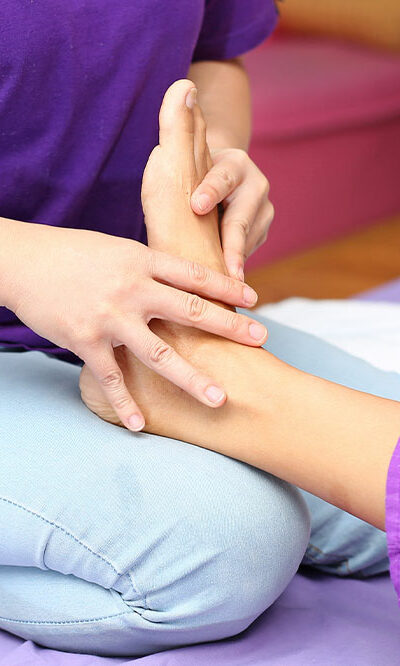
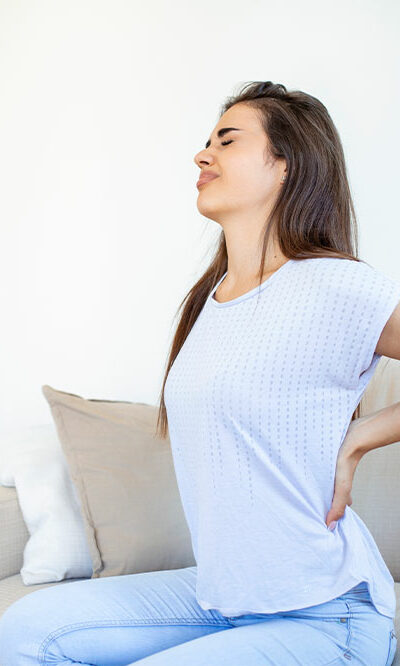
Excessive sugar intake has far-reaching effects on the body, including the development of diabetic neuropathy. Understanding and recognizing the signs and symptoms of this condition are crucial for early detection and effective management. Exploring the various signs of diabetic neuropathy helps empower one to address them proactively. From tingling and numbness in the extremities to digestive issues, sexual dysfunction, and even cognitive impairment, it is important to delve into each sign in detail. Tingling and numbness in extremities One of the earliest signs of diabetic neuropathy is the sensation of tingling and numbness in the extremities. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves responsible for transmitting sensory signals, resulting in abnormal sensations in the hands, feet, legs, and arms. If one experiences a “pins and needles” feeling or a loss of sensation, monitoring these changes and promptly seeking professional advice is essential. Burning sensation and pain Diabetic neuropathy can also cause persistent burning sensations or pain in the affected areas. The damaged nerves may send faulty signals to the brain, leading to constant feelings of heat or aching discomfort. This pain can be particularly bothersome at night, disrupting sleep and affecting the overall quality of life. Recognizing and addressing these sensations early on is key to managing diabetic neuropathy effectively. Muscle weakness and lack of coordination As diabetic neuropathy progresses, it can impact motor nerves, resulting in muscle weakness and a decline in coordination. Tasks that require fine motor skills, like buttoning a shirt or gripping objects tightly, may become increasingly challenging. Muscle weakness and a loss of balance can hinder mobility. This makes regular physical assessments and targeted exercises to improve strength and coordination even more important. Digestive issues Diabetic neuropathy can affect the nerves that control the digestive system, leading to a range of gastrointestinal symptoms. Bloating, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, and difficulty swallowing can arise due to disrupted nerve signals.